Blend mode
Updated: 08/26/2025
Summary
The blend mode is a function related to object composition.
While previous versions of Cubism supported simple compositing such as “Add” and “Multiply” under the name of blend method, Cubism 5.3 has been expanded to allow advanced compositing like the paint tool.
In blend mode, you can set Color Blend, which is RGB-related composition, and Alpha Blend, which is alpha-related composition.
Combining these blends makes it possible to create expressions that were not possible with the previous versions of Cubism.
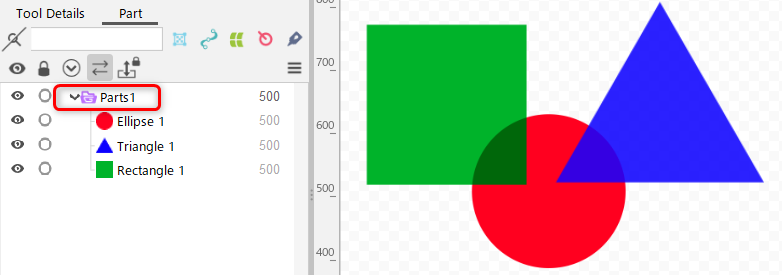
| Color Blend (1) Overlay (2) Screen | Alpha blend |
 |  |
Target objects
The blend mode is set on an object-by-object basis.
The following two types of objects can be set.
- ArtMesh
- Part (when offscreen drawing is enabled)
Inspector configuration
Settings are made in the inspector palette.
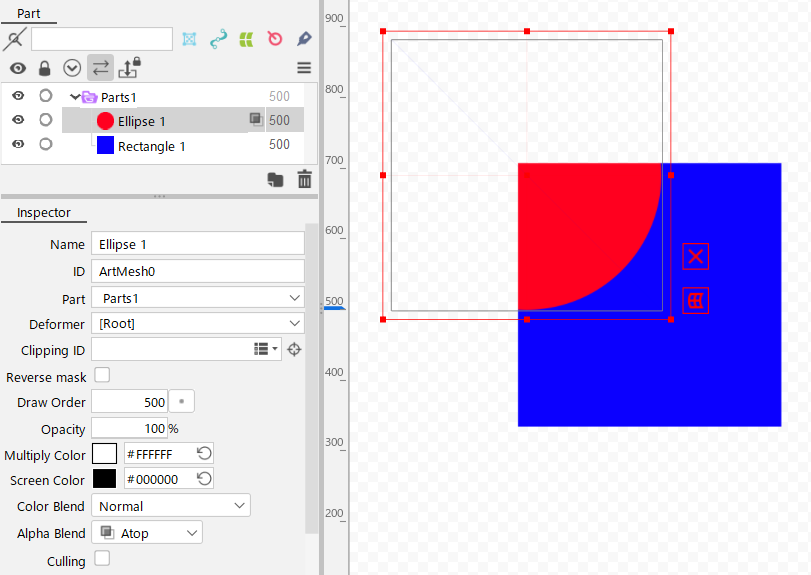
| Number | Item | Details |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | Color blend | Change the compositing method regarding the RGB of the selected object. You can select the method from among those listed under “Compositing Methods.” If the object is a part, you can set it by enabling offscreen drawing. |
| (2) | Alpha blend | Change the compositing method regarding the alpha of the selected object. You can select the method from among those listed under “Compositing Methods.” If the object is a part, you can set it by enabling offscreen drawing. |
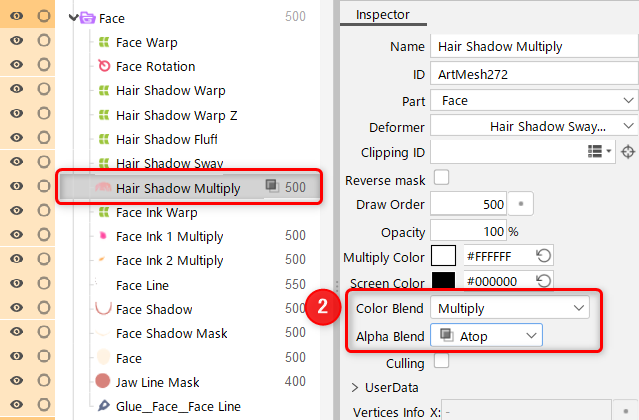
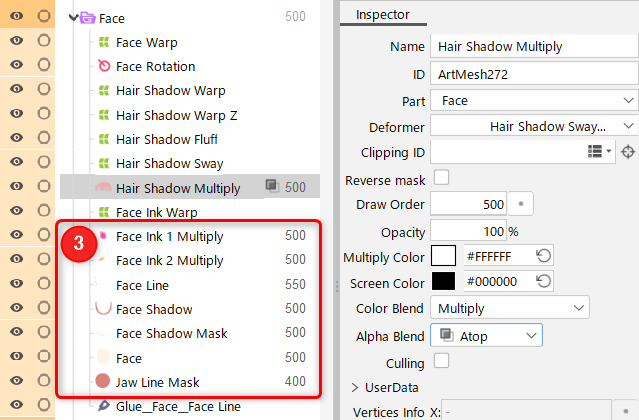
Example setup method
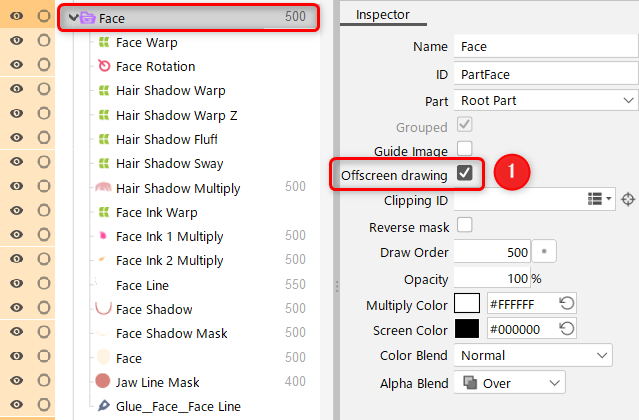
- Enable [Offscreen drawing] (1) for the parent part of the object for which you want to set the blend mode.
- Set the blend mode (2) for the object.
- In the part (3), compositing is performed on the objects with a lower draw order than the object with the blend mode set.
| Enable offscreen drawing. | Set the blend mode. | Composite on objects in the part. |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
Precautions
The object for which alpha blending is to be set is intended to be placed within a part for which offscreen drawing is enabled.
Also, within the part where offscreen drawing is enabled, all objects in a lower draw order than the object with the blend mode set will be affected.
PSD import and export
The ArtMesh color blend feature supports PSD import and export.
The rendering mode set in Photoshop can be imported directly as a blend mode in the Editor.
The blend mode set in the Editor can also be directly applied to Photoshop’s rendering mode.
However, PSDs drawn in rendering modes that are not supported by the Editor are imported with “Normal.”
PSD import and export are not supported for non-ArtMesh color blending.
Alpha blend does not support PSD import and export.
All PSDs are imported with “Over.”
Display on the Part(s) palette
Objects with Alpha blend set to anything other than “Over” will display the icon of the alpha blending set on the Parts palette.
If you wish to hide the icon, you can do so from [Alpha blend] in the Palette menu of the [Part(s)] palette.
Compositing method
Color blend
Color blend supports the following compositing methods.
The blending methods in Cubism 5.2 or earlier composited in a premultiplied format, whereas the color blend composites in a straight format.
However, this does not apply to “Add (Before 5.3)” or “Multiply (Before 5.3).”
Normal
Displays the color of the object on the canvas.
By default, this checkbox is selected.
Add
Adds the color of the object to the color on the canvas.
The brightness is reduced to account for overflow when the color is added.
Add (Glow)
Adds the color of the object to the color on the canvas but does not consider overflow.
This makes the color brighter than with the Add method.
Darken
Compares the color of the object to the color on the canvas and displays the darker color.
Multiply
Multiplies the color of the object by the color on the canvas.
The overlapped area will be a darker color.
Color burn
Darkens the color on the canvas for composition.
Darker areas will be even darker, resulting in stronger contrast.
Linear burn
Darkens the color on the canvas for composition.
Compared to the Color burn method, the overall color is darker and less peculiar.
Lighten
Compares the color of the object to the color on the canvas and displays the brighter color.
Screen
The effect is as if the color of the object is multiplied by the color on the canvas.
Unlike the Multiply method, the overlapped area becomes brighter.
Color dodge
Brightens the color on the canvas for composition.
Contrary to the Color burn method, the contrast is weaker.
Overlay
Multiplies if the color on the canvas is dark; composites with Screen if this color is bright.
Soft light
Composites in the same way as the Color burn method if the color of the object is dark and in the same way as the Color dodge method if this color is bright.
Hard light
Composites in the same way as the Multiply method if the color of the object is dark and in the same way as the Screen method if this color is bright.
Linear light
Reduces the brightness for composition if the color of the object is dark and increases the brightness if the color of the object is bright.
Hue
To create the color to be displayed, combines the Luminosity and Saturation of the color on the canvas with the Hue of the color of the object.
Color
To create the color to be displayed, combines the Luminosity of the color on the canvas with the Hue and Saturation of the color of the object.
Add (Before 5.3)
This is the “Add” method in Cubism 5.2 or earlier.
The name has been changed to distinguish it from the newly added “Add” method.
This method adds colors in a premultiplied format.
If this compositing method is selected, the setting of Alpha blend is ignored.
Multiply (Before 5.3)
This is the “Multiply” method in Cubism 5.2 or earlier.
The name has been changed to distinguish it from the newly added “Multiply” method.
This method multiplies colors in a premultiplied format.
If this compositing method is selected, the setting of Alpha blend is ignored.
Alpha blend
Alpha blend supports the following compositing methods.
Over
Combines the alpha on the canvas with the object’s alpha.
By default, this checkbox is selected.
Atop
Uses the alpha on the canvas.
The overlapping object will look clipped.
| Over | Atop |
 |  |
The edge of the mask can be made to look cleaner than the edge of a normal clipping mask.
| Clipping ID | Atop |
 |  |
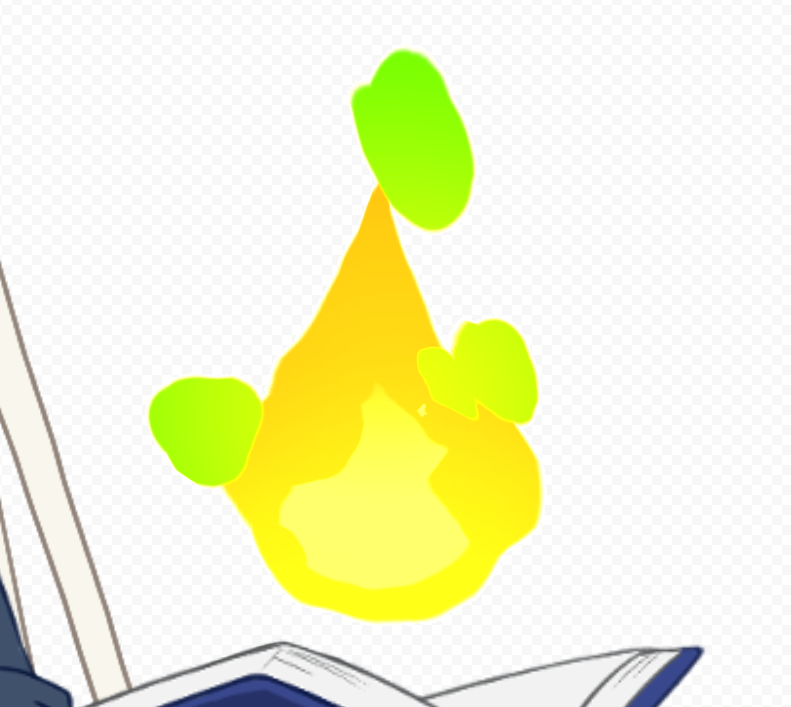
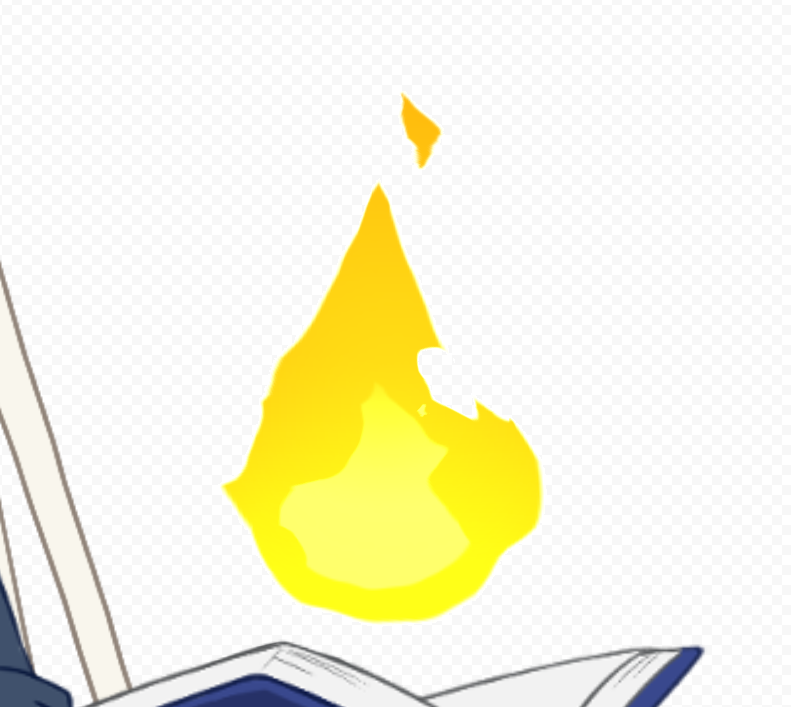
Out
Multiplies the alpha on the canvas by the inverted value of the object’s alpha.
It looks as if the object has been cut out of the picture on the canvas.
| Over | Out |
 |  |
Conjoint
Compares the alpha with that of the lower object to composite so that the alpha is the larger one.
For example, if an object with 30% opacity is overlapped by an object with 60% opacity, the overlapped area will have 60% opacity.
“Over” will make the lower object visible through the upper object, while “Conjoint” will not make the lower object, which has lower opacity, visible.
| Over | Conjoint |
 | 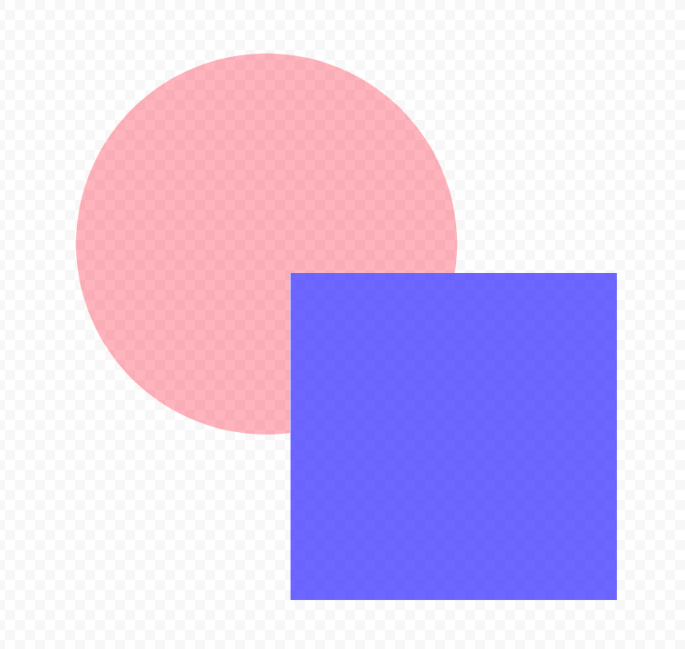 |
If an object with 60% opacity is overlapped by an object with 30% opacity, the overlapped area will also have 60% opacity.
The appearance of the overlapped area will look thinner than the “Over” appearance.
| Over | Conjoint |
 |  |
Disjoint
Composites so that the alpha is added to that of the lower object.
For example, if an object with 30% opacity is overlapped by an object with 60% opacity, the alpha of the overlapped area will be added, resulting in a darker and more pronounced appearance.
| Over | Disjoint |
 |  |
When line and fill objects are separated and gaps are visible between them, “Disjoint” can be used to make it look as if the gaps are filled.
| Over | Disjoint |
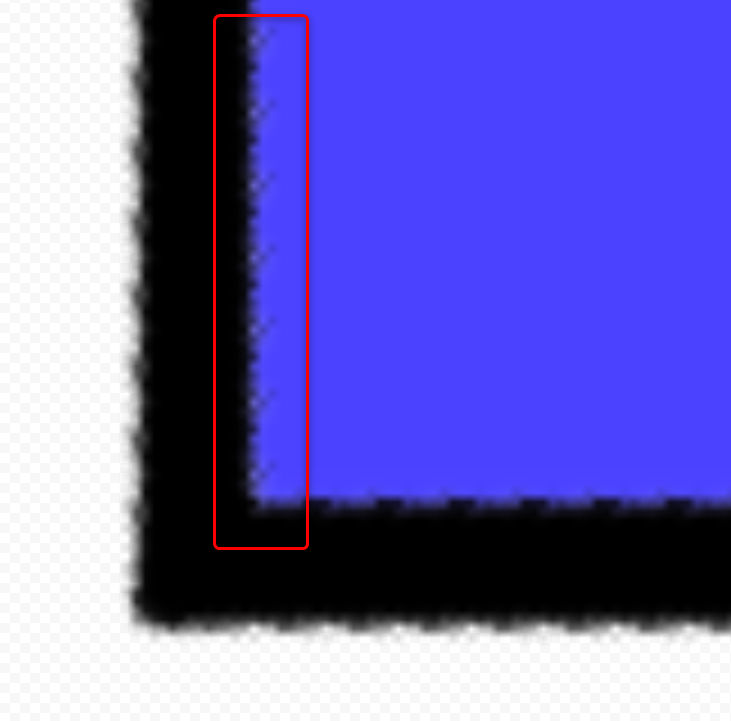 |  |
Tips
Color blends other than “Normal,” “Add (Before 5.3),” and “Multiply (Before 5.3)” and alpha blends other than “Over” are treated as “advanced blend modes.”
Precautions
Flickering due to overlapping polygons
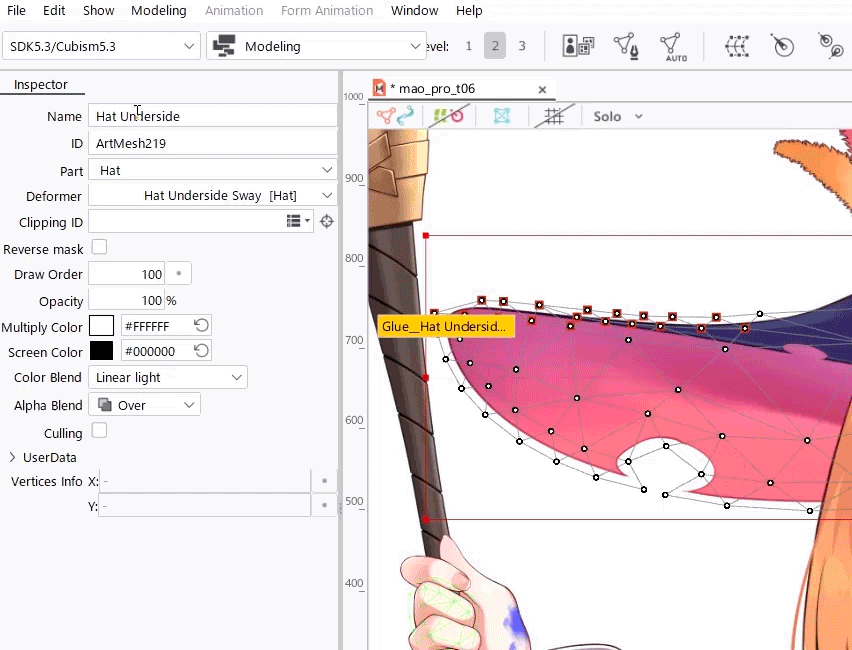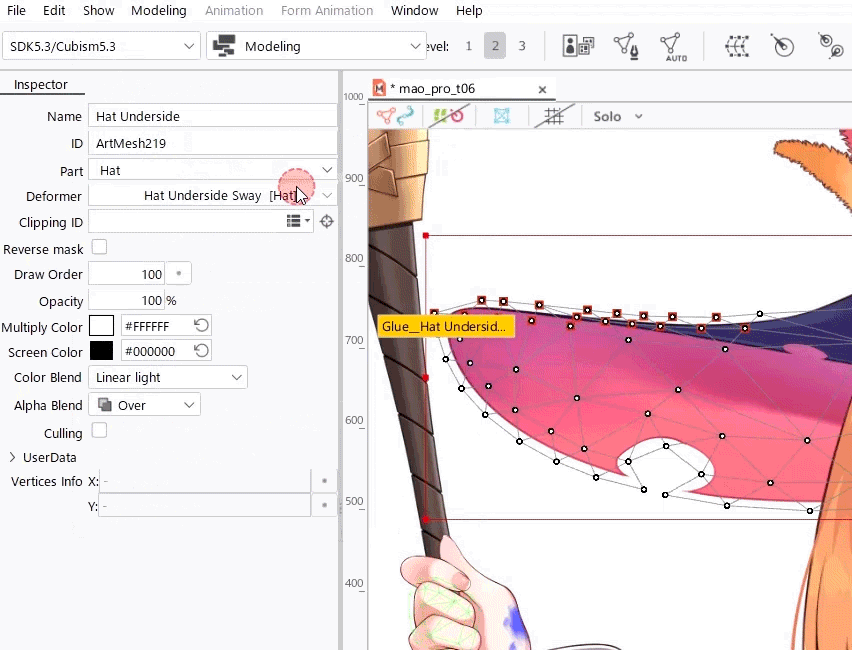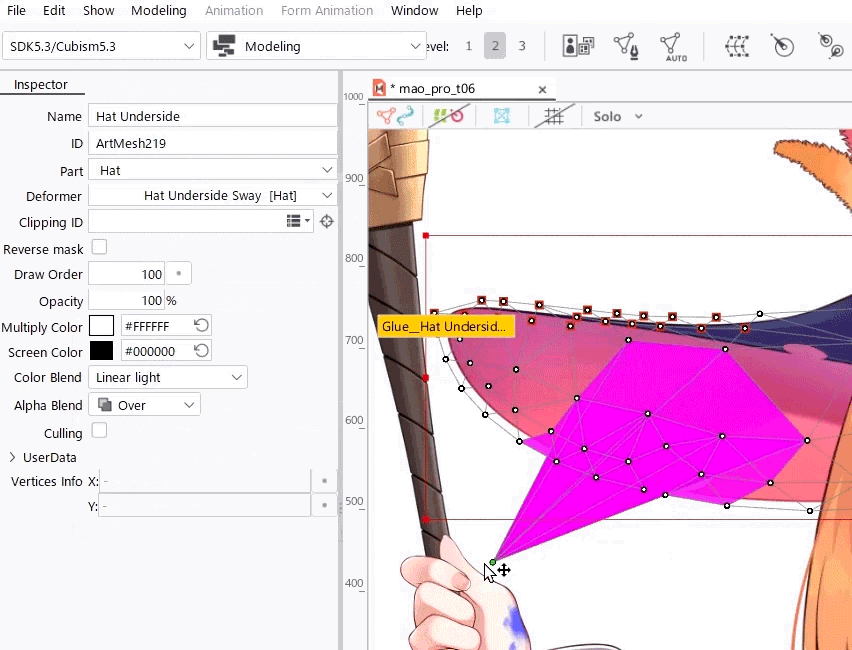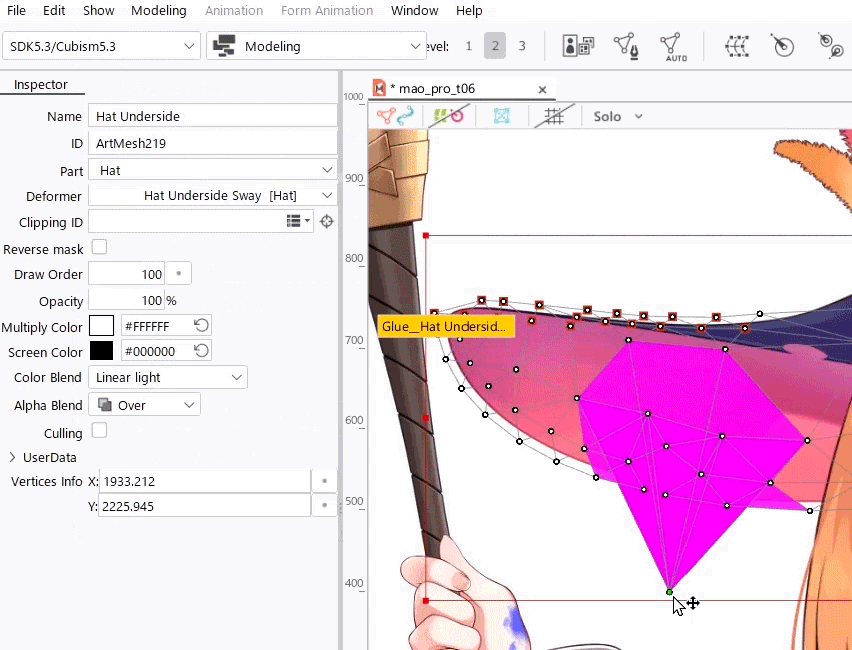
When you use an advanced blend mode, deforming overlapping polygons in a single mesh may cause flickering due to technical issues.
Therefore, when you use an advanced blend mode, be careful not to overlap polygons.
Flickering does not occur when the blend mode is set to “Normal” and “Over,” “Add (Before 5.3),” or “Multiply (Before 5.3).”
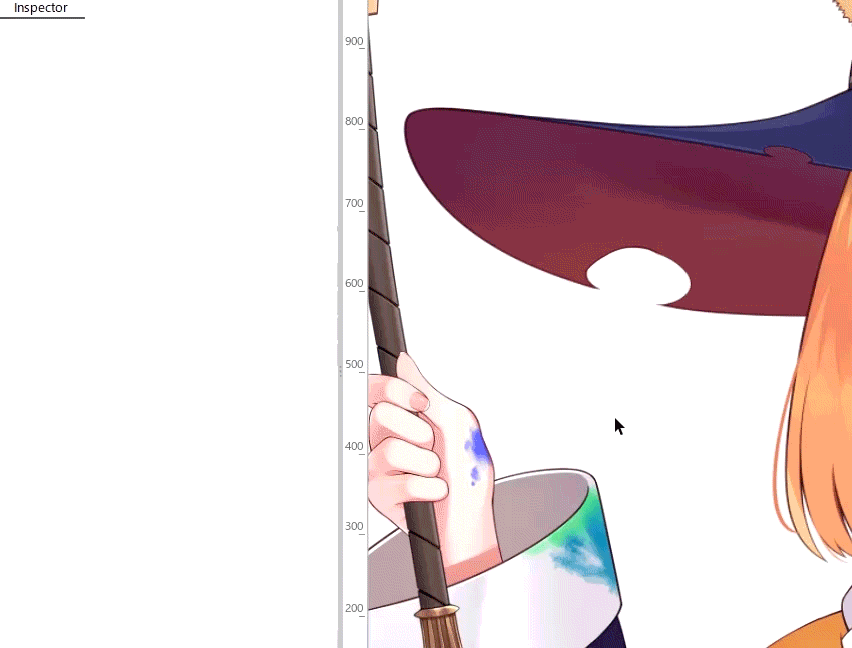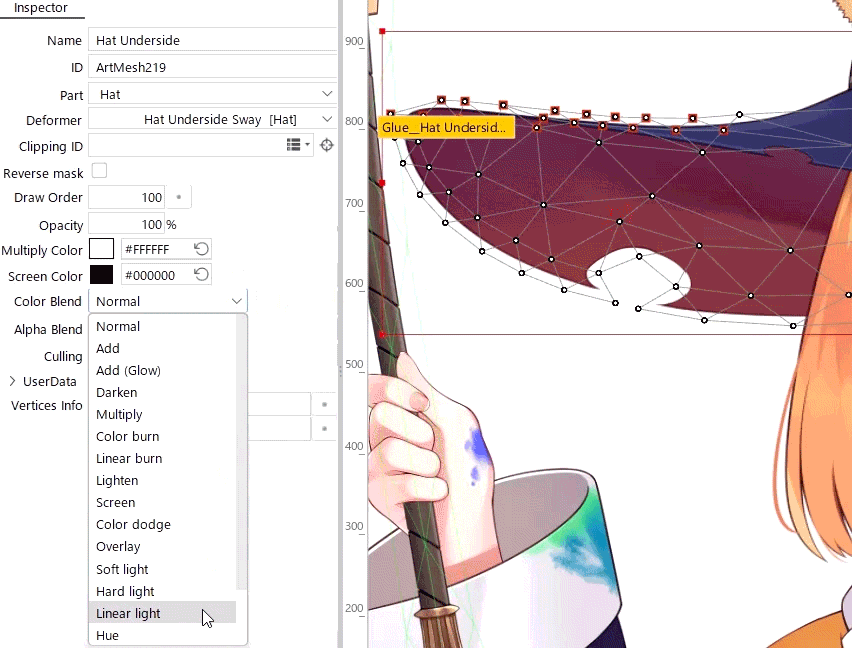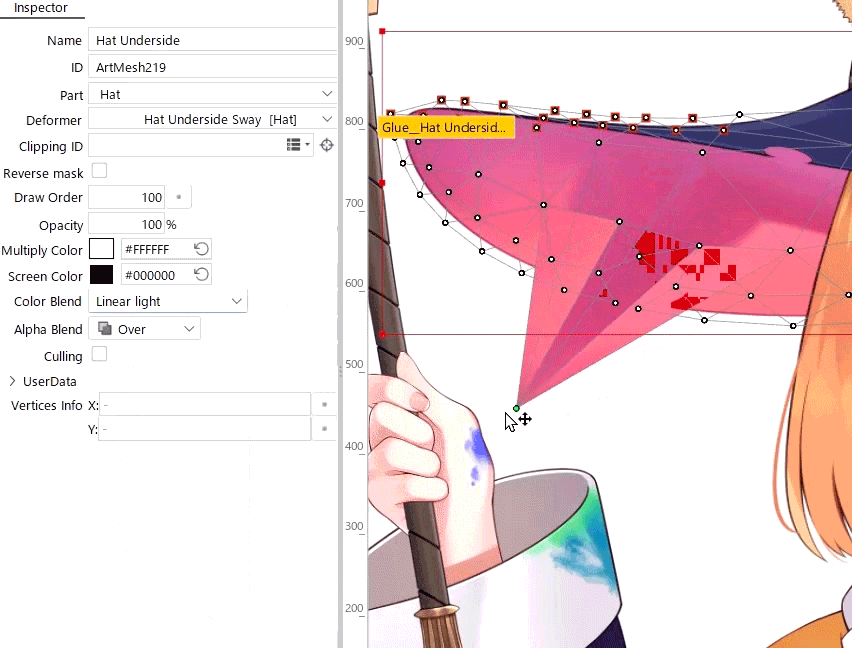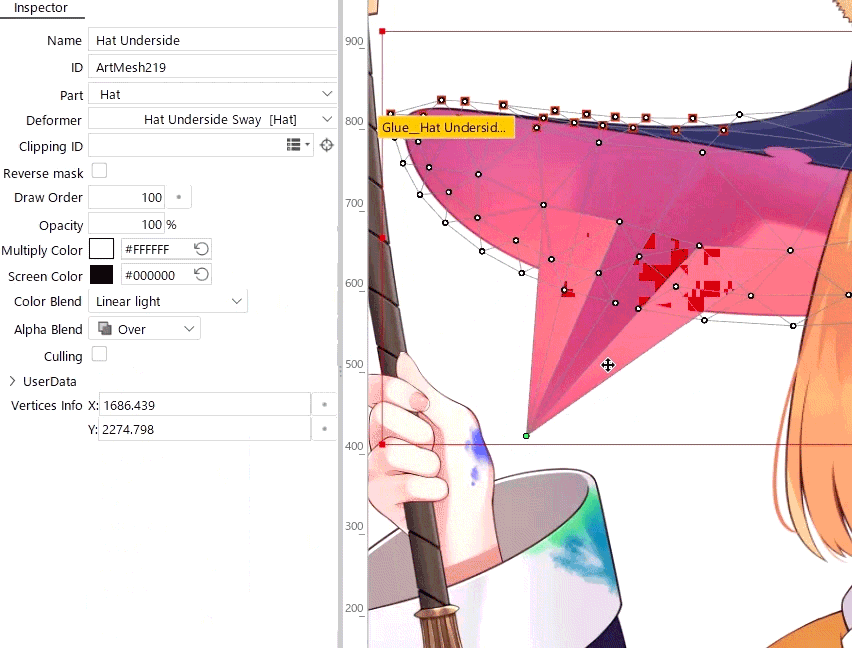
For easier viewing, in the [Show] menu, enable [Highlight overlapping polygons] to highlight overlapping polygons in an ArtMesh with advanced blend mode settings.
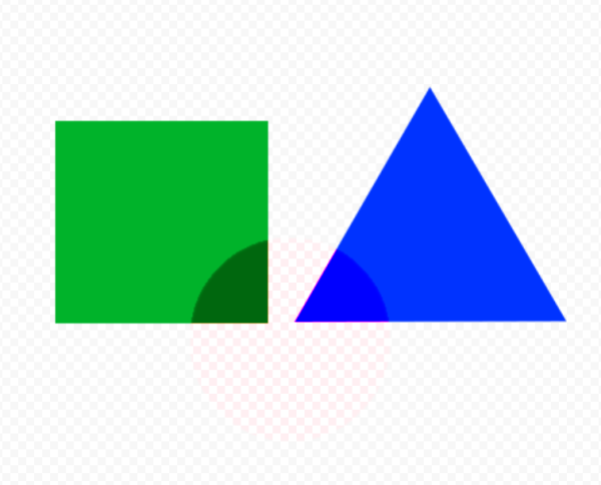
Effect of the Canvas
In blend mode, the compositing process is affected by the underlying canvas, resulting in the appearance of a composite with the canvas.
In the example below, the color blend of the middle circular ArtMesh is set to “Overlay,” but it looks as if it is composited with the checkerboard pattern of the canvas below the circle.
Alpha blending is similarly affected by the canvas.
To avoid the effect of the canvas, place a part with offscreen drawing enabled and place the objects within it.