蒙版前处理方法(Java)
最終更新: 2024年1月18日
在Cubism 5 SDK及更高版本中,部分类名等已变更。
有关详细信息,请参考CHANGELOG。
在Live2D Cubism SDK for Java中,为了保持智能手机等的绘制速度,在模型绘制处理开始时,采用了为一个蒙版缓冲区绘制所有蒙版形状的“预处理方法”。
在原理绘制方法中,每次绘制需要蒙版的Drawable时,都会绘制蒙版形状(见图)。
使用这种方法,每次Drawable需要蒙版时,都会发生切换渲染目标和清除缓冲区等相对高成本的处理。
因此,它可能会导致智能手机等上的绘图速度降低。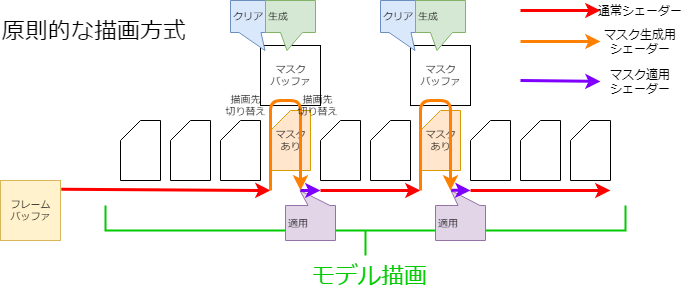
但是,仅仅提前准备好蒙版需要多个蒙版缓冲区,这会给内存记忆带来压力。
为了解决这个问题,可以对一个蒙版缓冲区进行以下处理,在将其视为正在使用多个蒙版缓冲区的同时,减少内存记忆压力。
蒙版集成
由于所有的蒙版都是预先生成的,因此接受相同蒙版指定的Drawable可以通过使用相同蒙版图片以减少生成的张数。
这个处理在CubismRendererAndroid.initialize函数调用中通过ACubismClippingManager.initialize函数完成。
@Override
public void initialize(
CubismRenderer.RendererType type,
CubismModel model,
int maskBufferCount
) {
renderTextureCount = maskBufferCount;
// 渲染纹理清除标志数组的原始化
clearedMaskBufferFlags = new boolean[renderTextureCount];
final int drawableCount = model.getDrawableCount(); // 绘制物件的数量
final int[][] drawableMasks = model.getDrawableMasks(); // 用于蒙版绘制物件的绘制物件索引列表
final int[] drawableMaskCounts = model.getDrawableMaskCounts(); // 用于蒙版绘制物件的绘制物件的数量
// 注册所有使用剪贴蒙版的绘制物件。
// 剪贴蒙版通常仅限于几个。
for (int i = 0; i < drawableCount; i++) {
if (drawableMaskCounts[i] <= 0) {
// 没有使用剪贴蒙版的图形网格(大多数情况下不使用)
clippingContextListForDraw.add(null);
continue;
}
// 检查是否与已有的ClipContext相同。
T_ClippingContext cc = findSameClip(drawableMasks[i], drawableMaskCounts[i]);
if (cc == null) {
// 如果不存在相同的蒙版则生成。
cc = (T_ClippingContext) ACubismClippingContext.createClippingContext(
type,
this,
drawableMasks[i],
drawableMaskCounts[i]
);
clippingContextListForMask.add(cc);
}
cc.addClippedDrawable(i);
clippingContextListForDraw.add(cc);
}
}
使用多个蒙版纹理
Cubism SDK for Java R1 beta1或更高版本中,您可以任意使用多个蒙版纹理。
因此,即使给模型设置了超过alpha1之前存在的36个蒙版上限的蒙版,也能够在SDK上正常显示。
但是,如果使用两个或多个蒙版纹理,则可以为一个蒙版纹理生成的蒙版上限数量为32个。
(仅使用一个蒙版时的蒙版上限数量为36个。相关详情会在之后说明。)
如果使用两个蒙版纹理,则可以使用的蒙版上限数量为32 * 2 = 64个。
使用多个蒙版纹理的设置如下。
int maskBufferCount = 2; CubismRenderer renderer = CubismRendererAndroid.create(); renderer.initialize(cubismModel, maskBufferCount);
如果没有传递给CubismRendererAndroid.initialize()的第二参数,则只会生成并使用一个蒙版纹理。
renderer.initialize(cubismModel);
按颜色信息分开
蒙版缓冲区是一个RGBA视频数组,与通常的纹理缓冲区等一样。
通常的蒙版处理仅使用此A通道来应用蒙版,而不使用RGB通道。
因此,通过在RGBA中具有单独的蒙版数据,一个蒙版缓冲区可以作为四个蒙版缓冲区处理。
分割分开
当4张蒙版图片不够用时,通过2等份、4等份和9等份处理蒙版缓冲区来增加蒙版数量。
由于还存在按颜色信息分割的情况,因此最多可以保存4 × 9、共36个不同蒙版。
此外,为防止蒙版图片被压扁,请使用应用蒙版的所有Drawable矩形绘制蒙版。
因此,需要生成范围、蒙版、使用蒙版生成矩阵。
使用多个蒙版纹理时,分割方法与仅使用一个蒙版纹理时相同。
但是,当使用多个蒙版纹理时,每个蒙版纹理的蒙版分配会尽可能平均分配,因此即使使用相同的模型也可以提高绘制质量。(如果增加蒙版纹理,则成本会相应增加)
例如,拥有32个蒙版的模型通常使用一个蒙版纹理绘制32个蒙版,但使用2个蒙版纹理时的蒙版分配为“每个16个”。
检查矩形
在蒙版生成的第一步中,对于每个蒙版,检查完全覆盖蒙版的矩形。
public void calcClippedDrawTotalBounds(CubismModel model, T_ClippingContext clippingContext) {
// 被剪贴蒙版(要添加蒙版的绘制物件)的全体矩形
float clippedDrawTotalMinX = Float.MAX_VALUE;
float clippedDrawTotalMinY = Float.MAX_VALUE;
float clippedDrawTotalMaxX = -Float.MAX_VALUE;
float clippedDrawTotalMaxY = -Float.MAX_VALUE;
// 判断该蒙版是否真的需要。
// 如果至少可以使用一个使用该剪贴的“绘制物件”,则需要生成蒙版。
final int clippedDrawCount = clippingContext.clippedDrawableIndexList.size();
for (int clippedDrawableIndex = 0; clippedDrawableIndex < clippedDrawCount; clippedDrawableIndex++) {
// 查找使用蒙版的绘制物件的绘制矩形。
final int drawableIndex = clippingContext.clippedDrawableIndexList.get(clippedDrawableIndex);
final int drawableVertexCount = model.getDrawableVertexCount(drawableIndex);
float[] drawableVertices = model.getDrawableVertices(drawableIndex);
float minX = Float.MAX_VALUE;
float minY = Float.MAX_VALUE;
float maxX = -Float.MAX_VALUE;
float maxY = -Float.MAX_VALUE;
int loop = drawableVertexCount * VERTEX_STEP;
for (int pi = VERTEX_OFFSET; pi < loop; pi += VERTEX_STEP) {
float x = drawableVertices[pi];
float y = drawableVertices[pi + 1];
if (x < minX) minX = x;
if (x > maxX) maxX = x;
if (y < minY) minY = y;
if (y > maxY) maxY = y;
}
if (minX == Float.MAX_VALUE) {
continue; // 由于无法获得任何有效点,因此跳过
}
// 应用到全体矩形
if (minX < clippedDrawTotalMinX) clippedDrawTotalMinX = minX;
if (maxX > clippedDrawTotalMaxX) clippedDrawTotalMaxX = maxX;
if (minY < clippedDrawTotalMinY) clippedDrawTotalMinY = minY;
if (maxY > clippedDrawTotalMaxY) clippedDrawTotalMaxY = maxY;
}
if (clippedDrawTotalMinX == Float.MAX_VALUE) {
clippingContext.isUsing = false;
csmRectF clippedDrawRect = clippingContext.allClippedDrawRect;
clippedDrawRect.setX(0.0f);
clippedDrawRect.setY(0.0f);
clippedDrawRect.setWidth(0.0f);
clippedDrawRect.setHeight(0.0f);
} else {
clippingContext.isUsing = true;
float w = clippedDrawTotalMaxX - clippedDrawTotalMinX;
float h = clippedDrawTotalMaxY - clippedDrawTotalMinY;
csmRectF clippedDrawRect = clippingContext.allClippedDrawRect;
clippedDrawRect.setX(clippedDrawTotalMinX);
clippedDrawRect.setY(clippedDrawTotalMinY);
clippedDrawRect.setWidth(w);
clippedDrawRect.setHeight(h);
}
}
颜色分开、分割分开的编排决定
确定每个蒙版所属的蒙版缓冲区的颜色通道和分割位置。
@Override
public void setupLayoutBounds(int usingClipCount) {
final int useClippingMaskMaxCount = renderTextureCount <= 1
? CLIPPING_MASK_MAX_COUNT_ON_DEFAULT
: CLIPPING_MASK_MAX_COUNT_ON_MULTI_RENDER_TEXTURE * renderTextureCount;
if (usingClipCount <= 0 || usingClipCount > useClippingMaskMaxCount) {
if (usingClipCount > useClippingMaskMaxCount) {
// 发布蒙版数量限制的警告
int count = usingClipCount - useClippingMaskMaxCount;
cubismLogError(
"not supported mask count : %d\n[Details] render texture count: %d\n, mask count : %d",
count,
renderTextureCount,
usingClipCount
);
}
// 在这种情况下,每次清除并使用一个蒙版目标
for (int index = 0; index < clippingContextListForMask.size(); index++) {
T_ClippingContext cc = clippingContextListForMask.get(index);
cc.layoutChannelIndex = 0; // 反正每次都会被清除,所以可以设置为固定
cc.layoutBounds.setX(0.0f);
cc.layoutBounds.setY(0.0f);
cc.layoutBounds.setWidth(1.0f);
cc.layoutBounds.setHeight(1.0f);
cc.bufferIndex = 0;
}
return;
}
// 如果有1张渲染纹理,则将其分为9份(最多36张)
final int layoutCountMaxValue = renderTextureCount <= 1 ? 9 : 8;
// 尽可能使用一个RenderTexture来编排蒙版。
// 如果蒙版组数为4个或更少,则为RGBA各通道置入一个蒙版,如果为5以上、6个以下,则将RGBA置入为2,2,1,1。
// NOTE:由于您希望计算每个蒙版的分割数,因此进位取整。
final int countPerSheetDiv = (usingClipCount + renderTextureCount - 1) / renderTextureCount; // 每张渲染纹理分配多少张纸
final int reduceLayoutTextureCount = usingClipCount % renderTextureCount; // 编排数量减一的渲染纹理数量(仅该数量的渲染纹理位对象范围)。
// 按顺序使用RGBA。
final int divCount = countPerSheetDiv / COLOR_CHANNEL_COUNT; // 一个通道中要置入的基本蒙版
final int modCount = countPerSheetDiv % COLOR_CHANNEL_COUNT; // 剩余,逐一分配到该编号的通道(非索引)
// 准备RGBA各通道(0:R, 1:G, 2:B, 3:A)
int curClipIndex = 0; // 按顺序设置
for (int renderTextureIndex = 0; renderTextureIndex < renderTextureCount; renderTextureIndex++) {
for (int channelIndex = 0; channelIndex < COLOR_CHANNEL_COUNT; channelIndex++) {
// 在该通道上编排的数量
// NOTE:编排数量 = 置入1个通道上的基本蒙版 + 1个用于额外蒙版的附加通道
int layoutCount = divCount + (channelIndex < modCount ? 1 : 0);
// 当编排数量减一时决定使用哪个通道
// 当div为0时,调整到正常索引范围
final int checkChannelIndex = modCount + (divCount < 1 ? -1 : 0);
// 如果这是对象通道并且存在编排数量减一的渲染纹理时
if (channelIndex == checkChannelIndex && reduceLayoutTextureCount > 0) {
// 如果当前渲染纹理是对象渲染纹理,则将编排数量减少1张。
layoutCount -= !(renderTextureIndex < reduceLayoutTextureCount) ? 1 : 0;
}
// 决定如何分割。
if (layoutCount == 0) {
// 什么都不做。
} else if (layoutCount == 1) {
// 直接使用所有内容。
T_ClippingContext cc = clippingContextListForMask.get(curClipIndex++);
cc.layoutChannelIndex = channelIndex;
csmRectF bounds = cc.layoutBounds;
bounds.setX(0.0f);
bounds.setY(0.0f);
bounds.setWidth(1.0f);
bounds.setHeight(1.0f);
cc.bufferIndex = renderTextureIndex;
} else if (layoutCount == 2) {
for (int i = 0; i < layoutCount; i++) {
final int xpos = i % 2;
T_ClippingContext cc = clippingContextListForMask.get(curClipIndex++);
cc.layoutChannelIndex = channelIndex;
csmRectF bounds = cc.layoutBounds;
// 2等份并使用UV
bounds.setX(xpos * 0.5f);
bounds.setY(0.0f);
bounds.setWidth(0.5f);
bounds.setHeight(1.0f);
cc.bufferIndex = renderTextureIndex;
}
} else if (layoutCount <= 4) {
// 4等份并使用
for (int i = 0; i < layoutCount; i++) {
final int xpos = i % 2;
final int ypos = i / 2;
T_ClippingContext cc = clippingContextListForMask.get(curClipIndex++);
cc.layoutChannelIndex = channelIndex;
csmRectF bounds = cc.layoutBounds;
bounds.setX(xpos * 0.5f);
bounds.setY(ypos * 0.5f);
bounds.setWidth(0.5f);
bounds.setHeight(0.5f);
cc.bufferIndex = renderTextureIndex;
}
} else if (layoutCount <= layoutCountMaxValue) {
// 9等份并使用
for (int i = 0; i < layoutCount; i++) {
final int xpos = i % 3;
final int ypos = i / 3;
T_ClippingContext cc = clippingContextListForMask.get(curClipIndex++);
cc.layoutChannelIndex = channelIndex;
csmRectF bounds = cc.layoutBounds;
bounds.setX(xpos / 3.0f);
bounds.setY(ypos / 3.0f);
bounds.setWidth(1.0f / 3.0f);
bounds.setHeight(1.0f / 3.0f);
cc.bufferIndex = renderTextureIndex;
}
}
// 超过蒙版限制数量时的处理
else {
int count = usingClipCount - useClippingMaskMaxCount;
cubismLogError(
"not supported mask count : %d\n[Details] render texture count: %d\n, mask count : %d",
count,
renderTextureCount,
usingClipCount
);
// 如果处于开发模式则停止。
assert false;
// 如果继续运行,SetupShaderProgram会出现过度访问,所以只能酌情插入。
// 当然绘制结果会不佳。
for (int i = 0; i < layoutCount; i++) {
T_ClippingContext cc = clippingContextListForMask.get(curClipIndex++);
cc.layoutChannelIndex = 0;
csmRectF bounds = cc.layoutBounds;
bounds.setX(0.0f);
bounds.setY(0.0f);
bounds.setWidth(1.0f);
bounds.setHeight(1.0f);
cc.bufferIndex = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
蒙版绘制,使用蒙版生成矩阵
根据绘制前检查的矩形范围及其所属位置,准备用于蒙版生成和蒙版使用的转变矩阵。
/*省略*/
// ---- 实际绘制一个蒙版 ----
T_ClippingContext clipContext = clippingContextListForMask.get(clipIndex);
csmRectF allClippedDrawRect = clipContext.allClippedDrawRect; // 使用该蒙版的所有绘制物件逻辑座标上的矩形边界
csmRectF layoutBoundsOnTex01 = clipContext.layoutBounds; // 包含此蒙版
final float margin = 0.05f;
float scaleX, scaleY;
final float ppu = model.getPixelPerUnit();
final float maskPixelWidth = clipContext.getClippingManager().getClippingMaskBufferSize().x;
final float maskPixelHeight = clipContext.getClippingManager().getClippingMaskBufferSize().y;
final float physicalMaskWidth = layoutBoundsOnTex01.getWidth() * maskPixelWidth;
final float physicalMaskHeight = layoutBoundsOnTex01.getHeight() * maskPixelHeight;
tmpBoundsOnModel.setRect(allClippedDrawRect);
if (tmpBoundsOnModel.getWidth() * ppu > physicalMaskWidth) {
tmpBoundsOnModel.expand(allClippedDrawRect.getWidth() * margin, 0.0f);
scaleX = layoutBoundsOnTex01.getWidth() / tmpBoundsOnModel.getWidth();
} else {
scaleX = ppu / physicalMaskWidth;
}
if (tmpBoundsOnModel.getHeight() * ppu > physicalMaskHeight) {
tmpBoundsOnModel.expand(0.0f, allClippedDrawRect.getHeight() * margin);
scaleY = layoutBoundsOnTex01.getHeight() / tmpBoundsOnModel.getHeight();
} else {
scaleY = ppu / physicalMaskHeight;
}
// 找到生成蒙版时要使用的矩阵。
createMatrixForMask(isRightHanded, layoutBoundsOnTex01, scaleX, scaleY);
clipContext.matrixForMask.setMatrix(tmpMatrixForMask.getArray());
clipContext.matrixForDraw.setMatrix(tmpMatrixForDraw.getArray());
/*省略*/
蒙版缓冲区的动态大小变更

OpenGL ES 2.0渲染器提供了一个API,以在运行时变更蒙版缓冲区的大小。
目前,蒙版缓冲区的大小设置为256 * 256(像素)作为初始值,但如果要将蒙版生成区域切割成9张,则将在85 * 85(像素)的矩形区域内绘制的蒙版形状进一步放大,作为剪贴区域使用。
因此,剪贴结果的边缘会模糊或渗色。
作为解决方案,我们提供了一个 API,可以在程序执行时变更蒙版缓冲区的大小。
例如,通过将蒙版缓冲区的大小从256 * 256变更为1024 * 1024,如果将蒙版生成区域切成9张,则可以在341 * 341的矩形区域中绘制蒙版形状,因此,您还可以放大并将其用作剪贴区域,以消除剪贴结果边缘的模糊和渗色。
* 扩大蒙版缓冲区的大小 ⇒ 如果要处理的像素增加,速度会变慢,但绘制结果会很漂亮。
* 缩小蒙版缓冲区的大小 ⇒ 由于要处理的像素减少了,所以速度会更快,但是绘制结果会很脏。
public void setClippingMaskBufferSize(final float width, final float height) {
if (clippingManager == null) {
return;
}
// 在放弃副本前保存渲染纹理的数量
final int renderTextureCount = this.clippingManager.getRenderTextureCount();
// Destroy and recreate instances to change the size of MaskBuffer
clippingManager = new CubismClippingManagerAndroid();
clippingManager.setClippingMaskBufferSize(width, height);
CubismModel model = getModel();
clippingManager.initialize(
RendererType.ANDROID,
model,
renderTextureCount
);
}
预处理方法能提高性能的原因
作为移动终端特有的情况,GPU的Clear指令和渲染目标切换指令的处理成本可能高于其他指令。
在使用原理方法绘制时,会根据需要蒙版的Drawable数量执行这些处理成本较高的指令。
然而,在预处理方法的情况下,可以减少这些指令的执行次数,这有望提高在智能手机等上的性能。
我们正在进行一项实验以实际了解效果。
本实验的测量方法和结果请参考“蒙版前处理方法(Native)”中的“预处理方法能提高性能的原因”。
将蒙版处理切换为高清方法
每次绘制时生成蒙版的方法会影响低规格终端的性能。
但是,当画面质量比运行时的性能更重要时(例如最终输出为视频),此方法更适合。
在Cubism SDK for Java中,可以将蒙版处理切换为高清方式。
要切换到高清方法,请将true传递给以下API。
CubismRenderer.isUsingHighPrecisionMask()
