Setting up collision detection
Updated: 01/30/2020
This section describes how to obtain the model’s collision detection from the input coordinates.
The following explanation is based on the assumption that the project is the same as the project for which the [Import SDK – Place Models] was performed.
Although it is possible to use Unity’s Collider for collision detection, the following is an explanation of how to use the functionality included in the Cubism SDK.
Summary
The Cubism SDK uses a component called Raycast for collision detection.
The SDK includes a sample project called [Raycasting] that uses this component, so please refer to that as well.
/Assets/Live2D/Cubism/Samples/Raycasting
To set up Raycast, do the following three things.
- Attach Components to Perform Raycast
- Specify the ArtMesh to Be Used for the Collision Detection
- Get the Result of the Judgment from CubismRaycaster.Raycast
Attach Components to Perform Raycast
Attach a component called [CubismRaycaster], which handles collision detection, to the GameObject that will be the root of the model.
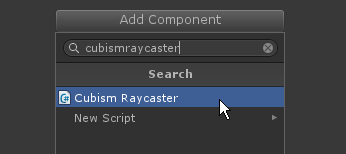
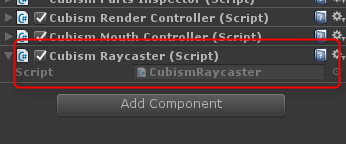
Specify the ArtMesh to Be Used for the Collision Detection
GameObjects that manage each ArtMesh to be drawn are located under [Model]/Drawables/.
The name of the GameObject is the ID of its parameters.
Attach [CubismRaycastable] to this GameObject that will be used as the range for the collision detection.
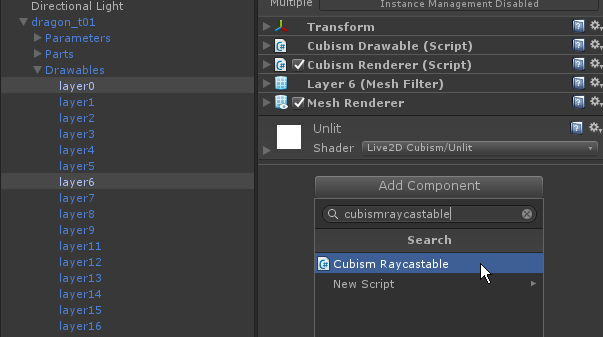
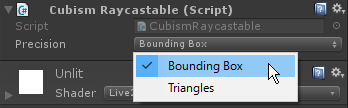
From CubismRaycastable, you can choose the range of collision detection for the attached mesh.
– Bounding Box: The rectangle surrounding the mesh is used for the collision detection. The load is lighter than with Triangles.
– Triangles: The shape of the mesh is used for the collision detection. If you want to determine the range accurately, please use this setting.
Get the Result of the Judgment from CubismRaycaster.Raycast
Finally, use Raycast() on the CubismRaycaster attached to the root of the model to get the result of the collision detection.
Create a C# script called “CubismHitTest,” add the code as follows, and attach it to the root of the model.
using UnityEngine;
using Live2D.Cubism.Framework.Raycasting;
public class CubismHitTest : MonoBehaviour
{
private void Update()
{
// Return early in case of no user interaction.
if (!Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
{
return;
}
var raycaster = GetComponent<CubismRaycaster>();
// Get up to 4 results of collision detection.
var results = new CubismRaycastHit[4];
// Cast ray from pointer position.
var ray = Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition);
var hitCount = raycaster.Raycast(ray, results);
// Show results.
var resultsText = hitCount.ToString();
for (var i = 0; i < hitCount; i++)
{
resultsText += "n" + results[i].Drawable.name;
}
Debug.Log(resultsText);
}
}
This completes the setup.
In this state, clicking on a mesh to which CubismRaycastable is attached in the Game View during execution will output the result of the collision detection to the Console View.
Example
3
layer0
layer2
layer6
